Automatic Initialization and Updating for TIMESTAMP and DATETIME : MYSQL
I’ve been searching for an efficient way to set created and modified date fields in MySQL.And I found the solution by updating the date and time manually. however, I wanted to find a way to automatically do this on the database layer.
The approach I take here is a combination of using the TIMESTAMP field data type and a TRIGGER
IMPORTANT: When using multiple TIMESTAMP fields in a table, there can be only one TIMESTAMP column with CURRENT_TIMESTAMP in DEFAULT or ON UPDATE clause. This is why we need to use a TRIGGER to update one of the fields values.
In our case, we will set the date_modified field to contain the DEFAULT of CURRENT_TIMESTAMP and also set the ON UPDATE clause to CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
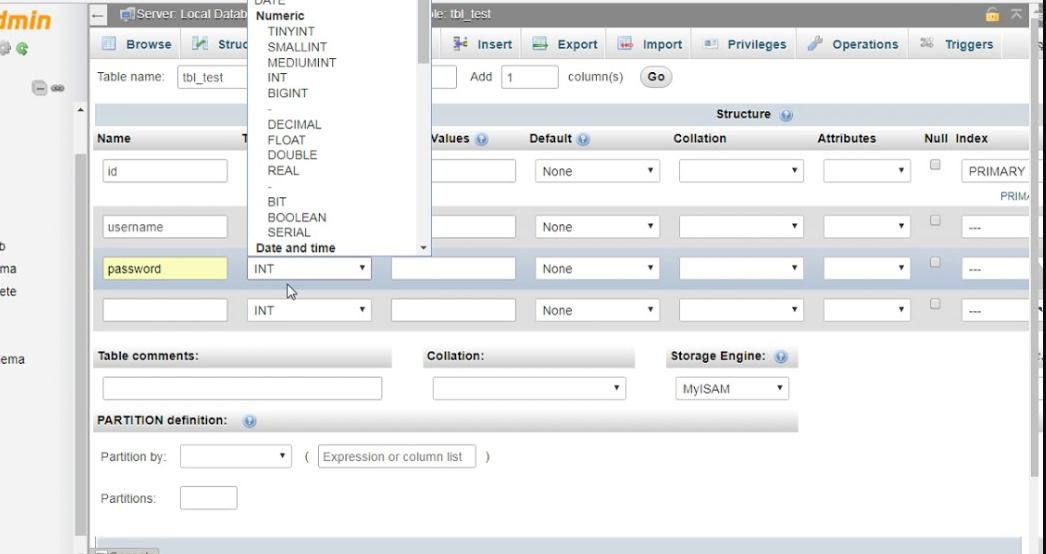
CREATE TABLE `batch` (
`batch_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`batch_name` int(11) NOT NULL,
`batch_description` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`creation_date` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`updation_date` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`batch_id`,`batch_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `batch_id_UNIQUE` (`batch_id`)
)
ENGINE = InnoDB;
If you noticed in the CREATE TABLE snippet above we use the TIMESTAMP features on the date_modified field, but set our date_created field to NULL by default. We do this because our TRIGGER will populate the value before the insert.
DELIMITER //
CREATE TRIGGER temp_before_insert_created_date BEFORE INSERT ON `temp`
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
SET NEW.date_created = CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
END//
DELIMITER ;
In our trigger, we simply set the date_created value to the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.
Now you will be able to insert and update rows in your table without having to specify the date_created or date_modified values.
INSERT INTO `batch` (batch_name) VALUES ('2074');
UPDATE `batch` SET field_value = '2075';
Another approach that can be used is by setting the date_created value to NULL when inserting a row. This involves a different CREATE TABLE syntax.
CREATE TABLE `batch` (
`batch_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`batch_name` int(11) NOT NULL,
`batch_description` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`date_created` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`date_modified` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
ENGINE = InnoDB;
Notice our date_created field is now set to NOT NULL with a default value of 0000-00-00 00:00:00. Here’s an important note from the documentation:
TIMESTAMP columns are NOT NULL by default, cannot contain NULL values, and assigning NULL assigns the current timestamp.
In other words, when we insert and set the value to NULL on a TIMESTAMP field, it will insert the current timestamp.
An example insert/update statement would look like:
INSERT INTO `batch` (batch_name, date_created) VALUES ('2074', NULL);
UPDATE `batch` SET field_value = '2075';
This approach allows us to avoid using triggers, however requires you to specify the NULL value when the query is executed.